If you’re looking for track lighting, you must have heard about 1 or 3 circuits or phases already. On this page, Olam lighting will explain the difference between those two.
What’s the 4-Wire 3-Cirucit(Phase)?
A “4-wire 3-circuit” system in track lighting is a specific type of electrical track configuration commonly used for more complex lighting setups. Here’s a detailed explanation:
- 4 Wires: The system includes four wires. These typically consist of three live (or “hot”) wires, each corresponding to a separate circuit (L1, L2, L3), and one neutral wire (N).
- 3 Circuits (or Phases): The three live wires represent three distinct circuits or phases. Each circuit can be controlled independently, allowing different sets of lights on the same track to be switched on or off, or dimmed separately. This feature provides greater flexibility in lighting control and design.
- Application: The 4-wire 3-circuit system is often used in commercial or retail environments where varied and adaptable lighting is required. For instance, different sections of a store may need different lighting at various times, which can be easily managed with this system.
- Installation and Compatibility: Fixtures and accessories for this system must be compatible with the 4-wire 3-circuit configuration. Installation might be more complex than simpler systems (like a 1-phase track) and typically requires professional handling.
- Advantages: This setup allows for more elaborate lighting designs, enabling users to create different ambiances or focus on certain areas within the same space using the same track.
In summary, a 4-wire 3-circuit track lighting system offers a high level of control and flexibility, making it ideal for settings where lighting needs vary within a single space.
What is a Circuits (phase)?
In a standard power cable with three veins, you’ll find a phase, a neutral wire and a protective earth/ground wire.
The phase is the wire that’s under voltage relative to the neutral and protective wire. The phase leads the electrical current, together with the neutral wire, from and to connected equipment.
In a typical power cable that contains three veins, you will find a phase wire, a neutral wire, and a protective earth or ground wire. The phase wire carries voltage in comparison to the neutral and protective wires. It, along with the neutral wire, is responsible for directing the flow of electrical current to and from the connected equipment.
![What is the difference between 1 phase and 3 phase track? 1]()
![What is the difference between 1 phase and 3 phase track? 2]() 1 phase vs. 3 phases
1 phase vs. 3 phases
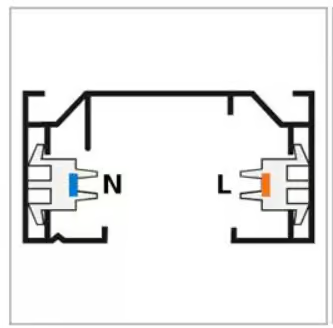
In a single-phase (1-phase) rail, also known as a 1-circuit rail, electricity flows between two wires: the phase wire (L for line) and the neutral wire (N). As a result, all lighting fixtures on this rail are linked together, meaning they can only be switched on or off simultaneously.
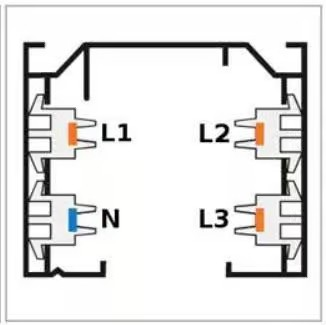
Conversely, 3-phase rails consist of three phases (L1, L2, L3), each of which can be connected individually with the neutral wire (N). This setup allows for three distinct circuits on the same track, enabling separate control for each circuit.
To utilize all three circuits on the rail, the track must be connected to a power cable that contains five veins.
The difference between 1-phase and 3-phase track lighting lies primarily in their electrical configurations and the flexibility they offer in lighting control.
1-Phase Track (Single Phase Track)
- Electrical Configuration: In a 1-phase track, all the track lights are connected to a single circuit. This means they all share the same electrical phase.
- Control: Since all lights are on the same circuit, they can only be turned on or off simultaneously. There is no option to control individual lights or groups of lights separately.
- Application: 1-phase tracks are typically used in residential settings or smaller commercial spaces where complex lighting configurations are not required.
- Installation: Generally simpler and more cost-effective to install compared to 3-phase tracks.
3-Phase Track (Three Phase Track)
- Electrical Configuration: In a 3-phase track, there are three separate circuits within the same track, each corresponding to a different electrical phase. This allows lights to be connected to any of the three phases.
- Control: You can control lights connected to different phases independently. This means you can turn on/off or dim lights in one phase without affecting lights in the other phases.
- Application: 3-phase tracks are ideal for commercial and retail spaces where there is a need for flexible and variable lighting setups, such as highlighting different products or areas at different times.
- Installation: More complex and potentially more costly to install due to the additional wiring and control mechanisms.
In summary, the choice between 1-phase and 3-phase track lighting depends on the level of control and flexibility required in the lighting setup, as well as the intended application and installation complexity.

Advantages and Disadvantages
While both single-phase and three-phase track systems have their merits, at dmLights, we have a preference for the three-phase system. We’ll guide you through both the benefits and drawbacks of this system.
Advantages of 3 Phase Rails
- Multiple Circuits with Independent Control: As previously mentioned, 3 phase rails offer the ability to create three separate circuits, each of which can be controlled independently. This feature allows for greater flexibility in lighting design and control.
- Wider Selection of Fixtures: The variety of lighting fixtures available for 3 phase systems is significantly larger than that for 1 phase systems. This gives users more options to choose from to suit their specific needs.
- Ease of Installation: Installing a 3 phase rail tends to be easier. These rails provide more space to conceal cables, which is not only convenient but also enhances the overall aesthetics. Due to their larger size, they can also more effectively cover the holes through which connection cables exit. Additionally, 3 phase rails are more robust and stable compared to 1 phase rails.
- Versatility in Usage: A 3 phase rail doesn’t necessarily have to be used for three separate circuits; it can also function as a 1 phase rail (or even 2 phase, though less common). By connecting L1, L2, and L3 together, you can make all spots on the rail function identically, regardless of the switch position, similar to a 1 phase rail.
- Higher Power Support: A 3 phase rail can support three times the power of a 1 phase rail. This feature is particularly beneficial in settings like stores, where many spots are needed on long rails, requiring more power distribution.
These advantages make 3 phase rails a versatile and practical choice for various lighting applications, especially in commercial and retail environments.

Disadvantages of 3 Phase Rails
- Higher Cost: 3 phase rails are generally more expensive compared to 1 phase rails. This increased cost can be a consideration for those on a tight budget.
- Aesthetic Considerations: From an aesthetic perspective, 3 phase systems may appear less refined. This is primarily due to the presence of a switch on their base, used for selecting the phase for connection. This feature can impact the overall sleekness of the design.
What specifications of Track does OLAMLED Track light use?
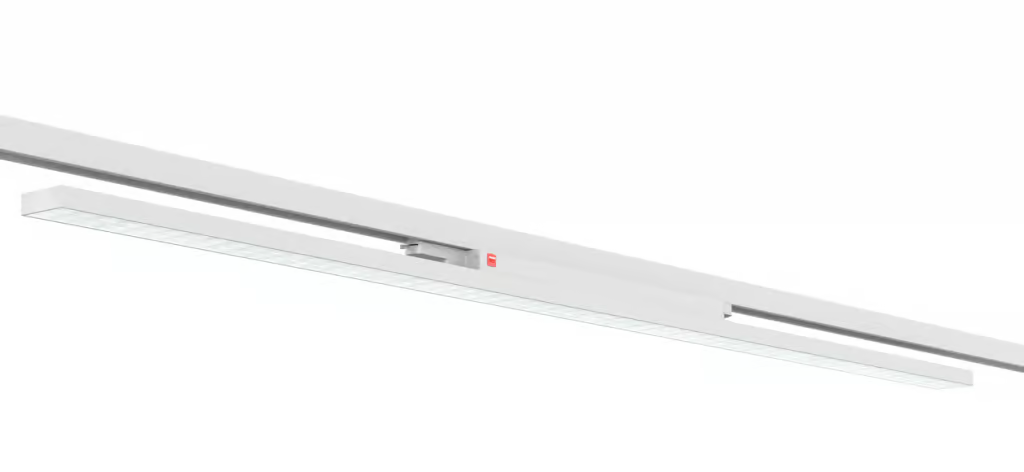
OLAMLED’s track panel lights and track linear lights utilize 4-wire, 3-circuit track adapters. This design is compatible with the majority of track systems used in Europe, offering simplicity and convenience in installation and application.
Including the current models and specifications of OLAMLED’s track panel lights. To get detailed and up-to-date information on the models and specifications of OLAMLED’s track linear lights, I recommend visiting OLAMLED’s official website or contacting their customer service directly. They will be able to provide you with a comprehensive list of their track lighting products, including models, specifications, features, and any other relevant information.




