Lighting is a vital aspect of our lives that often goes unnoticed. It affects our health, productivity, and even our mood.
Good lighting can make us feel more energized and motivated, while poor lighting can cause eyestrain and headaches. However, the quality of light goes beyond just its brightness or intensity.
The ability of a light source to portray colors accurately is also critical, and this is where the Color Rendering Index (CRI) comes in.
In this blog post, we will delve into what is CRI in lighting, how it affects lighting and the benefits of high CRI lighting. We will also explain why you must choose OlamLED for your LED lighting needs.

What is Color Rendering Index (CRI)?

· Explanation of CRI
Color Rendering Index (CRI) is a measurement of a light source’s ability to imitate the colors of various objects accurately and realistically when compared to a reference source, typically natural sunlight.
The CRI is expressed on a scale of 0 to 100, with a higher CRI indicating that the colors of objects illuminated by the light source appear more natural and vivid.
· How CRI is measured
The CRI is determined by comparing the color appearance of test colors when illuminated by the measured light source to their appearance under a reference illuminant, typically natural daylight.
Traditionally, the test colors consist of eight pastel colors selected to represent a range of hues and saturations. However, a more recent method, TM30-2015, employs 99 colors to deliver a more precise and thorough assessment of color rendering.
The difference between the color appearance of the test colors under the reference illuminant and the measured light source is used to calculate the CRI.
Here are the steps you need to follow to measure CRI Index as per CIE standards:
- First, you must select the reference light source, typically daylight (for 5000K color temperature or above) or a blackbody radiator for under 5000K color temperature. The reference light source is used as a benchmark for color rendering, so choosing the appropriate one for the application is vital.
- Next, select the test light source from which to measure the CRI. The test light source should have the same color temperature as the reference light source.
- The next step is to prepare the color samples for testing. There are fifteen color samples in total, as per CIE standards, which represent a range of hues and saturations. However, you can only use the first eight for comparison.
- Now it’s time to measure the reference light source’s spectral power distribution (SPD) using a spectroradiometer. The SPD is a graph that shows the intensity of each wavelength of light emitted by the source.
- Repeat step 4 for the test light source. This will give you two SPD graphs that you can compare.
- The next step is to measure the color rendering properties of the test light source using the color samples. Place each sample under both the reference and test light sources, and measure the reflectance spectra of each sample using a spectrophotometer. The reflectance spectra show how much light the sample reflects at each wavelength.
- Calculate the color rendering index (CRI) using the data collected in steps 4-6. The CRI is a numerical value between 0 and 100, with higher values indicating better color rendering.
The formula for calculating CRI is as follows:
CRI = (R1 + R2 + … + R8) / 8
Where R1 to R8 are the color rendering scores for each of the eight color samples. The Color Rendering Score is the difference between the color appearance of the sample under the reference light source and the test light source. Finally, interpret the results.
The CIE method is considered the standard measurement method for CRI because it provides a consistent and objective way to compare different light sources. It is widely used in the lighting industry to ensure products meet specific color rendering requirements.
· Scale of CRI

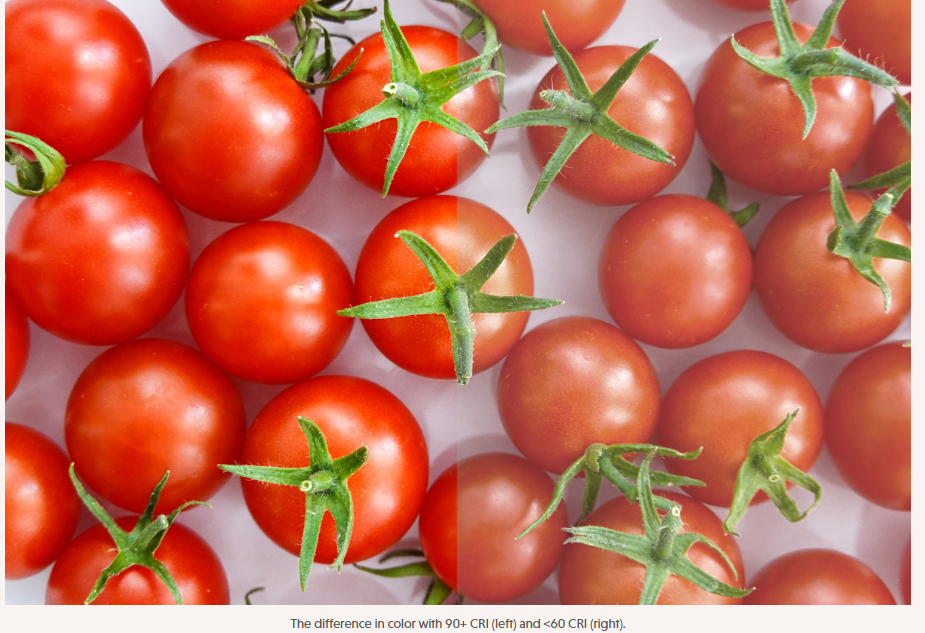
So, what is a Good CRI? As shown in the Color Rendering Index chart below, the scale of CRI ranges from 0 to 100, with a light source having a CRI of less than 60 is considered to have poor color rendering, while a score of 100 indicates that the light source can render colors accurately, with no color distortion.
A score of 0 indicates that the light source cannot render colors at all.
| CRI Score | Rating |
| 90-100 | Excellent (Most accurate color rendering) |
| 80-89 | Very Good (May have some color distortion) |
| 70-79 | Good (May have some color distortion) |
| 60-69 | Fair (May have some color distortion) |
| Below 60 | Poor (Obvious distortion in colors) |
· Importance of CRI in different settings
The importance of CRI can vary depending on the setting and the task being performed.
- Retail Settings: In retail settings, accurately representing product colors is essential for sales. A high CRI light source can help to accurately depict product colors, making them look more attractive and appealing to customers.
- Art Galleries and Museums: In settings where art is displayed, the color accuracy of the lighting can be critical. A high CRI light source can help accurately render the colors in a painting or sculpture, ensuring visitors can see the artwork as intended.
- Photography and Film: In photography and film, lighting plays a critical role in accurately representing the subject’s colors being photographed or filmed. A high CRI light source can ensure that the colors in the image are accurately captured and represented.
- Medical Settings: In medical settings, accurate color rendering can be essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. For example, accurate color rendering is critical in dermatology for assessing skin tones and spotting abnormalities.
How CRI impacts the perception of color and the human eye?
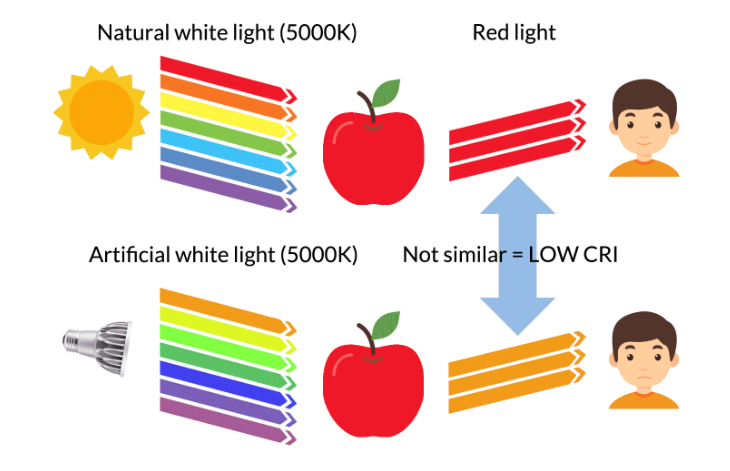
Here are some examples to help illustrate the concept of the Color Rendering Index (CRI):
Example 1: A high-quality LED light has a CRI of 95. When it illuminates a red object, it appears to be the same deep, rich shade of red as it would under natural sunlight. The same is true for all other colors. The color rendering is so accurate and good that it’s difficult to tell the difference between the LED light and natural sunlight. Therefore, LED light is among the best CRI light.
Example 2: A low-quality fluorescent light has a CRI of 50. When it illuminates a same red object, the object appears to have an orange-yellowish tint that it wouldn’t have under natural sunlight. The same is true for all other colors. The color rendering is poor, and objects can appear dull or washed out.
What is CRI in lighting of different types?
Here is an example of a Color Rendering Index table for different types of lighting:
| Light Source | CRI Score |
| Incandescent Bulbs | 95-100 |
| Halogen Bulbs | 95-100 |
| High-Pressure Sodium | 25-60 |
| LED Bulbs | 70-95 |
| Fluorescent Bulbs | 50-98 |
| Natural Daylight | 100 |
How to Choose Color Rendering Index for Your LED Lighting?
When selecting LED lighting for your home or business, it’s essential to consider the Color Rendering Index (CRI).
· Factors to ponder when choosing CRI for your LED lighting:
- The intended use of the lighting: Different applications require different levels of color accuracy. For example, if you are lighting an art gallery, you would want a high CRI to showcase the true colors of the artwork. On the other hand, if you are lighting a parking lot, a lower CRI may be sufficient.
- Personal preference: some people may prefer a warmer or cooler color temperature or may prioritize energy efficiency over color accuracy.
- Budget: higher CRI LEDs can be more expensive than those with lower CRI scores.
· The type of lighting scenarios that benefit from different CRI scores:

- High CRI (90+):- Ideal for settings where color accuracy is crucial, such as photography studios, art galleries, museums, and retail spaces.
- Medium CRI (80-90): suitable for most indoor applications, including homes, offices, and hospitality environments.
- Low CRI (<80): appropriate for outdoor and industrial settings, where color accuracy is less important than budget, energy efficiency, and durability.
· Importance of considering color temperature alongside CRI:
In addition to the CRI, it’s essential to consider the color temperature of the LED lighting.
The color temperature measures how warm or cool the light appears and is measured in Kelvin (K).
Warmer temperatures (below 3000K) create a cozy and relaxed atmosphere, while cooler temperatures (above 4000K) provide a brighter and more stimulating environment.
The ideal color temperature will depend on the intended use of the space and personal preference.
In conclusion,
The Color Rendering Index (CRI) is essential when selecting lighting for any space or application. The CRI score determines how accurately colors will be represented under the light source, impacting the perception of color and the overall ambiance of a room or environment.
At Olamled, we are committed to providing high-quality LED lighting products focusing on CRI. We understand the importance of accurate color rendering, and our products are designed to meet the specific needs of each lighting application, ensuring optimal performance and color accuracy.
We encourage our readers to choose lighting with a high CRI score for their specific lighting needs. By selecting lighting with a high CRI score, you can ensure that colors will be accurately represented, creating a comfortable and inviting environment.
Whether for a home, office, or commercial setting, the right lighting can make all the difference, and the CRI score is a crucial factor in achieving the perfect lighting for your space.



