Introduction
Zhaga Consortium plays a vital role in the LED lighting industry as it provides standardization, interoperability, and modularity between the different components of LED lighting. The Zhaga consortium’s efforts to create a dynamic ecosystem are seamless. By putting all the lighting manufacturers on the same page globally, they help the manufacturers and designers evolve in the LED lighting field.
If you look forward to learning more about the Zhaga Consortium and related information, you are in the right place. Let’s read below:

What is the Zhaga Consortium?
Zhaga Consortium is known for standardizing the LED components interfaces, comprising LED modules, LED holders, LED drivers, and LED light engines.
Zhaga Consortium works to streamline the supply chain of LED lighting and simplify the design and manufacturing of LED lighting fixtures. It develops specifications based on the components and the themes of smart lighting.
Significance of Standardization in Lighting Industry
Standardizing lighting fixtures in the lighting industry must be considered as it plays a vital role in ensuring the lighting products’ efficiency, interoperability, and safety. Some of the critical aspects of this standardization and its significance comprise the following:
Interoperability
When all lighting manufacturers follow standards, the lighting products of different manufacturers can work together without any problem. It is essential to introduce smart lighting systems in the lighting density.
The common standards that enable the integration of different components consist of opting for bulbs, fixtures, and sensors from other manufacturers.

Energy Efficiency
The standards in the lighting industry focus on energy and consider energy efficiency, and they prescribe the performance criteria for lighting products. The standards set guidelines for the lambs’ luminous efficacy, ensuring that lighting devices consume specific energy.
Quality Assurance
standardization also sets a benchmark for the quality standards followed by the lighting industry. Every manufacturer is bound to follow those standards so that reliable and durable products can be manufactured, benefiting the manufacturers and consumers.
Safety
The need to standardize safety concerns is also very important to ensure that the lighting products have minimal risk to users. These standards help to consider safety from fire hazards and protect the lighting equipment against other such hazards. The safety considerations ensure that both the consumers and the manufacturer are protected.
Regulatory Compliance
Different countries have a regulatory framework that makes the lighting products adhere to international standards, and complying with these standards ensures that the products are safe to use and can legally be sold worldwide.

History of Zhaga Consortium
Zhaga Consortium was founded in 2010 and has its roots in Germany. The founders of Zhaga Consortium include the major lighting industry manufacturers, including Tridonic, Osram, and Philips.
The main aim of the Zhaga Consortium was to develop and promote the specifications of the LED light and the components used. The interfaces were designed and standardized to cover LED luminaires’ thermal, mechanical, and electrical aspects to make it easier for the manufacturer to create interoperable lighting products.
The Zhaga approach separated the light source from the light fixture to make the replacement, maintenance and upgrades more manageable. Zhaga Consortium comprises a wide group of members from different parts of the world, including companies involved in manufacturing semiconductors and LED lighting. This collaboration at the global level ensures that the standards developed by Zhaga are accepted and adopted widely.
Zhaga has published its specification in a series called “Books,” each comprising specific aspects of standardizing LED components. These books cover the standardization of drivers, LED modules, sensors, and connectors for the manufacturers so that they can follow these while developing them.
As time passed, the consortium continued to evolve its standards to keep pace with technological advancements and meet industrial requirements. The consistent addition and updates of these specifications also reflect the lighting industry’s dynamic nature.
Objectives of Zhaga Consortium
The Zhaga Consortium’s goals are to address the LED lighting industry challenges and promote standardization. These objects include the following:
- The main objective of the Zhaga Consortium is to improve flexibility among the components of LED lighting. It defines standardized interfaces so that different LED components can work together without any problem.
- The consortium also standardizes the interface between different modules used in LED lighting and separates components, which include light sources and sensors. This module separation makes upgrades easier and also helps to maintain sustainability.
- Zhaga has also developed global standards reflected in the LED lighting components globally, which is achieved by collaborating with diverse industrial groups worldwide. Hence, a consistent framework is designed for LED products.
- Zhaga aims to move with innovation and efficiency in the LED lighting industry, and it provides a set of common standards; hence, manufacturers can focus on product differentiation and create innovative solutions.
- The consortium’s efforts have streamlined the process of development for the manufacturers. Due to the standard interfaces, it becomes easier to reduce the time-to-market for new LED lighting products.
- The evolution of LED technology helps adapt and incorporate the standards into technological advancements. The specifications of Zhaga support integrating new functionality and features in the LED lighting fixtures.
Essential Standards and Specifications of Zhaga Lighting
There are various standards and specifications of Zhaga Lighting, and these are discussed below:
Zhaga Book 3
These standards comprise the mechanical interfaces of the LED light engines and define the configuration of the LED modules to stay compatible with the sockets in luminaires.
Zhaga Book 7
The book 7 addresses the outdoor luminaire interfaces and specifies the characteristics of these in terms of thermal, electrical, and mechanical properties. The standard mainly focuses on street lighting applications.
Zhaga Book 12
The book 12 features the interfaces for the LED modules and defines their configuration and dimensions to facilitate interchangeability.
Zhaga Book 18
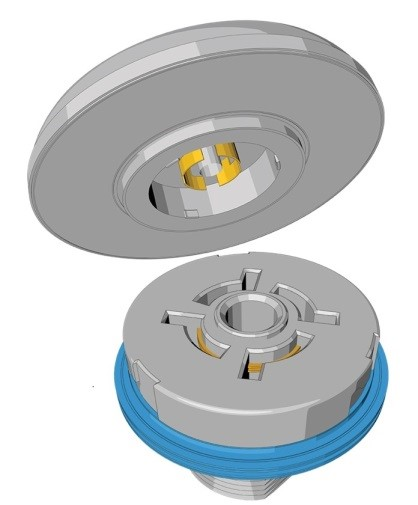
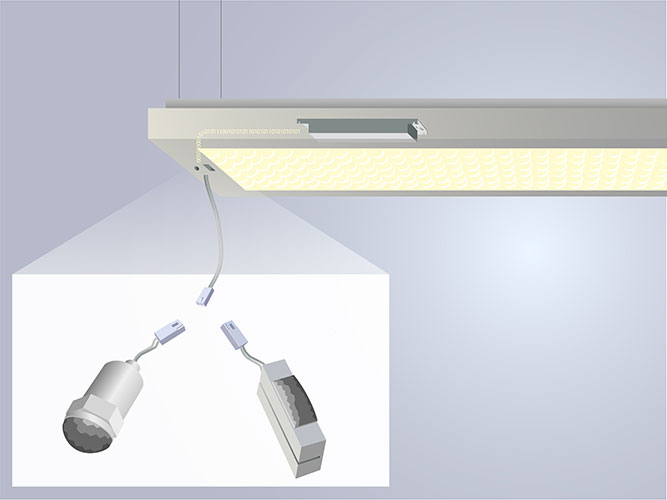
This book details the mechanical interface between the receptacle and the module and helps the vendor look for design innovation. The book 18 also recommends the electrical interference that considers a 4-pin connector, which enables the 24V DC power supply and the DALI control.
This standard complies with the ANSI and NEMA standards and describes the mating receptacles commonly used in the UK and USA. These modules compose a minimal footprint, and hence, the flexibility in the design of the luminaire is high.

Zhaga Book 20
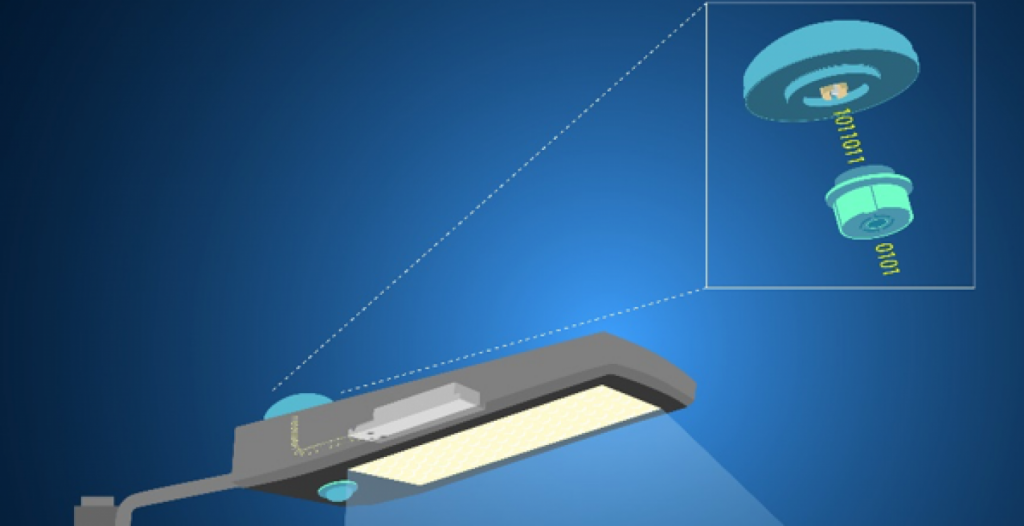
The book 20 offers standards for the interface between the indoor LED lighting fixture and the sensing node. The node is connected to the LED driver and control system and typically offers sensor input, allowing communication between network components.
Zhaga Book 21
The Zhaga book 21 describes the interface of LED modules with the thermal, mechanical, and electrical aspects and the integrated drivers. This aims to create standards for the driver integration for the LED modules, which helps increase the modularity.
Zhaga Book 24
The book 24 specifies the interface of outdoor LED luminaires with the light engine in a rectangular shape, and it also covers the thermal, mechanical, and electrical characteristics of these luminaires.
Zhaga Book 25
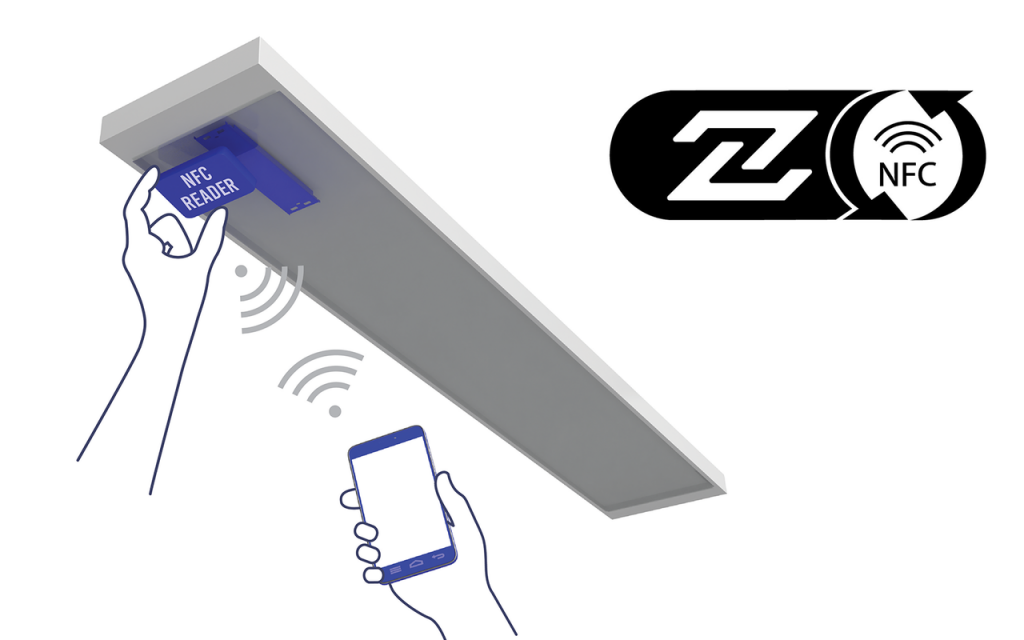
The book 25 includes mobile NFC readers with Bluetooth interface, which promotes maintenance and replicability. It also allows the manufacturers to implement communication between the lights and the smart devices without any need for a connection based on cable.
Zhaga D4i
The Zhaga D4i standards accommodate the lighting design, offering plug-and-play interoperability between the certified luminaires and control devices.
Zhaga Certification:
Zhaga certification offers a surety that all the products for lighting comply with the Zhaga standards, and it makes interoperability and interchangeability between the products of different manufacturers.
How To Get Zhaga Certified?
To become a member of Zhaga, you must pay the required fee and agree to Zhaga’s terms. You also need to ensure that the LED lighting products you manufacture are according to the standards provided by Zhaga, including the components.
Zhaga has methods to test and evaluate your products to see whether they meet the specified standards and provide you with the reports for the test. After your products have passed the test, they grab you the certification and a logo you can use.
Zhaga Product Database:
The Zhaga product database offers a platform that provides information about the products certified by Zhaga and that comply with the relevant standards. The manufacturers are allowed to register their products, which are also certified, so that they can offer a resource for the people who need components for manufacturing their lighting products, which are Zhaga compliant.
Impact of Zhaga on the Future of Lighting Industry
The Zhaga Consortium has a significant impact on the lighting industry, and this is expected to continue in the future as well in the following areas:
- The main objective of Zhaga is to emphasize the increased compatibility and interoperability between different components used in LED lighting. The manufacturers are working seamlessly, and in the future, it will pave the way for the system where flexibility will increase by promoting innovation, and the barriers will be reduced, making lighting systems adaptable for manufacturers and consumers
- Zhaga’s approach comprises a modular context, which allows for the separation of components, which increases upgrades and maintenance. Hence, a more future-proof lighting infrastructure can be achieved. As the industry advances, modular design principles will be adopted, and the lighting system will see a growth in innovation.
- The rise of intelligent lighting systems has made Zhaga’s efforts to standardize the sensors and interfaces. It boosts communication protocols and facilitates integrating innovative lighting solutions important in the intelligent lighting system landscape.
- Zhaga’s global standardization approach ensures that its specifications are internationally acceptable. This offers to harmonize and simplify the manufacturing process for the worldwide market, reducing the manufacturers’ cost and complexity.
- Zhaga also provides a framework for innovation that allows the manufacturers to focus on advanced features and, at the same time, maintain compatibility. It creates a culture of continuous improvement and ensures technological advancement in the industry.
- Zhaga focuses on lighting technologies that are energy efficient, and it helps to promote sustainability. Environmental concerns are becoming prominent, and Zhaga standards contribute to developing green lighting solutions.
- Zhaga is committed to adapting technological advancements in standards, and hence, the lighting industry can easily incorporate new features in its products by staying in touch with future developments.

Reasons to Adopt the Zhaga Standard
Many reasons may compel lighting manufacturers to adopt the Zhaga standards. Some of these reasons are discussed below:
- The supply chain improves due to the adoption of Zhaga standards as the supply chain bottlenecks are reduced since multiple suppliers offer the same level of components with the same level of compatibility. The LED light engine gets standardized to integrate the upgrades into existing luminaire designs.
- The interchangeable components will mean that there are a number of manufacturers available, and hence, there are many options for a wide variety of components.
- The standardized components also allow the creation of a luminaire with the same designs, but the attributes are different. The factors like color temperature, CRI, stability, and lumen output may vary with a similar design. Hence, the companies can provide a wide range of fixtures at different prices and performance categories despite the same design.
- The components can be used interchangeably; hence, the components allow the companies to produce different lighting fixtures, reducing the cost of prediction.
- The upgrades of LLEs will generally follow the same standards as the existing ones. Hence, the need to re-engineer the luminaire design will also be minimized when technology advances.
- The hassle of redesigning is eliminated when the new LLE is introduced. Hence, the new products can easily be brought to the market quickly.
- The components are designed with similar standards, and it allows the luminaries currently used with the future components. These upgrades on the components are possible with the LLEs that are interchangeable.
- The interchangeable components allow users to upgrade their existing lighting fixtures with the latest technology; hence, LED lighting is no longer a disposable product.
- The interchangeable parts have been available; the designers may use the same components for most designs. These components’ production will increase with time usage, and therefore, the components that do not follow the standards will eventually disappear.
- The luminaries since have a longer life span and can be used for a more extended period; hence, the demand for components will be maintained due to repair and services.
How To Join Zhaga as A Member?
Zhaga membership is open to every lighting manufacturing company. The companies that wish to become members of Zhaga should review the agreement for membership, and once the application form is filled out online, the process starts. You will get detailed information on the accessibility of your membership and also will get a logo once the registration process is completed.
Conclusion
The standards of Zhaga Consortium offer the entire lighting industry a framework to operate and manufacture its lighting products and components. These products and components are equipped with various benefits and are also equipped with technological advancements. The standards have ensured lighting components’ efficiency, usability, and interoperability.
FAQs:
1. What is Zhaga compliant?
Ans. Zhaga offers a consortium for companies working as global lighting manufacturers. It has been developing the standards for technical specifications that allow LED light sources from multiple suppliers to be interchanged without altering the product’s design.
2. What is a Zhaga socket?
Ans. Zhaga socket offers an interface for intelligently controlling street and outdoor lighting solutions.
3. What is the difference between Zhaga and NEMA?
Ans. Zhaga offers simple and safe controllers and sockets with no high voltage lines as they have 4-pin contacts. On the other hand, NEMA has controllers and receptacles, which are complex.
4. What is a Zhaga node?
Ans. Zhaga node offers monitoring of the status and dimming control for the lighting fixture as it comprises a built-in photocell for daylight-harvesting.
5. What is the difference between DALI 2.0 and D4i?
Ans. DALI 2.0 offers the standards for the interface between intra-luminaire communication, and the D4i standardized the LED driver for the intra-luminaire networks.



